Note. This section is based on Starburst documentation in mid 2023. Please check it for any updates and new features. Also note difference of Galaxy vs Enterprise, and different functionality for different connectors.
Starburst offers two platforms, Starburst Enterprise and Starburst Galaxy. Both platforms are built on the open-source software, Trino.
- Starburst Galaxy (available in Azure Marketplace – PaaS) is an easy-to-use, fully-managed, and enterprise-ready SaaS platform. You can use Starburst Galaxy to easily connect to and configure your data sources and query your data wherever it is stored. Starburst Galaxy manages everything else so you and your team can concentrate on data processing and analytics.
- Starburst Enterprise (available in Azure Marketplace, deploy to AKS – IaaS) platform (SEP) is a fully supported, enterprise-grade distribution of Trino. It adds more powerful integrations, improves performance, and provides security while simplifying deployment, configuration, and cluster management. SEP can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud.
- Trino (Formerly PrestoSQL, IaaS) is an open-source distributed SQL engine for running fast analytic queries against various data sources ranging in size from gigabytes to petabytes. Trino was designed and built from scratch for interactive analytics. It approaches the speed of commercial data warehouses while scaling to the size of very large organizations.
Features exclusive to Starburst Enterprise and Starburst Galaxy compared to Trino are following:
- Performance features: Materialized Views, Proprietary parallelized connectors, Starburst Warp Speed (indexing and caching for data lakes).
- Connectors: More than 50 supported enterprise connectors, Cross-cloud connectivity with Starburst Stargate for Starburst Enterprise, improved connectors for Oracle and Teradata, Client integrations for Power BI, Tableau, Thoughtspot, dbt etc.
- Security features: built-in, enterprise-grade access controls, data encryption and masking, query auditing, integrations with major third-party security and governance providers.
- Data management: Autoscaling, Data discovery (search capabilities), Data Products (curate and share data by business users).
- Professional Support
Some important considerations when selecting between Starburst Enterprise and Starburst Galaxy include the following:
- The people and skills available in your organization. Starburst Galaxy requires minimal expertise from data engineers or platform administrators. In contrast, Starburst Enterprise requires infrastructure, networking, data security, and governance expertise. However, the experience for data consumers is identical between the platforms.
- Security and governance in your organization. Starburst Galaxy includes a powerful access control system for authorization and supports SSO and built-in user management for authentication. Starburst Enterprise includes all those features and more, including integrations with authentication platforms (LDAP, Kerberos, OAuth) and authorization managers (Ranger, Privacera, Immuta).
- The data sources your organization will query. If connectors to your organization’s data sources are available in Starburst Galaxy, we recommend using Starburst Galaxy. However, Starburst Enterprise currently includes a broader variety of connectors to data sources. It can also be operated anywhere, even in your organization’s private network and
Starburst architectural components
Starburst Cluster is comprised of one coordinator and one or more worker nodes, the connectors for any data sources that will be queried, and catalogs specific to each connector that contain the configuration files for that connector.
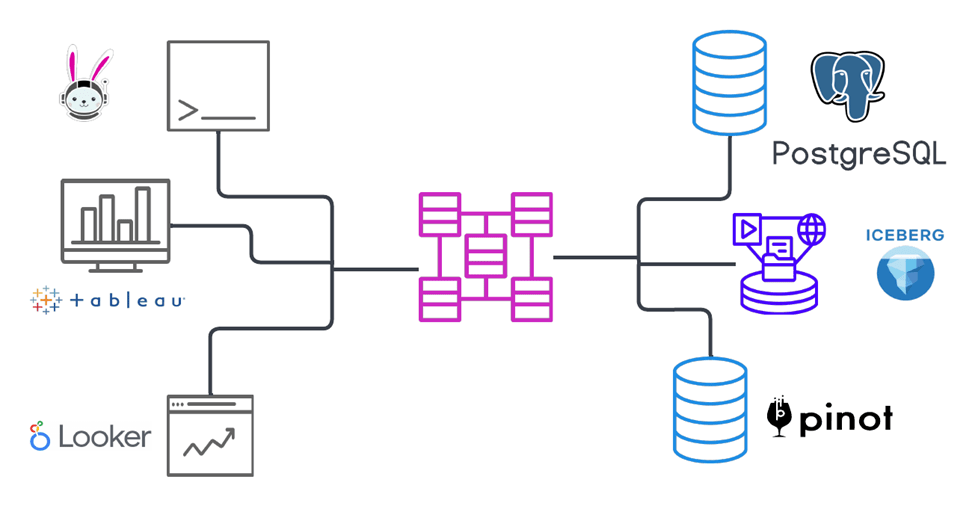
- Client – any tool that passes a SQL query to Starburst (Web UI, command line interfaces, programming languages, and business intelligence (BI) tools).
- Data Sources range from small RDBMSs to large, multiple-petabyte object stores. Additionally, Starburst platforms can federate across data sources, allowing you to access and join data from multiple data sources in the same query.
- Connectors allow Starburst platforms to communicate with data sources by connecting to those data sources through an interface. Each data source requires a specific connector. Together, Starburst platforms offer connectors for more than 50 data sources. Some of our connectors include Iceberg, Hive, Snowflake, and PostgreSQL.
- For non-object storage connectors, the query engine can rely on the data source for some of the query processing.
- For object-storage connectors, the query engine processes the entire query.
- Catalogs allow to define how Starburst platforms access a specific data source via a connector. Catalogs do this by configuring the properties of that connector. Each connector has a particular set of properties that can be configured. The configuration Starburst platforms use with a connector can change how the connector functions and which data it exposes to the Starburst platform. For this reason, Starburst platforms can include multiple catalog configurations for the same connector.
- Coordinator is a single server that handles incoming queries and provides query parsing and analysis, scheduling, and planning. It distributes processing tasks to worker nodes.
- The query engine leverages distributed, massively parallel processing (MPP) to process queries from the platform quickly and efficiently. This is accomplished by distributing the work required to complete a query across the worker nodes in a cluster. This means work can be accomplished more quickly because it can be completed in parallel rather than sequentially.
- Worker is a single server that executes tasks as directed by the coordinator, including retrieving data from the data source via the connector and processing data.

The coordinator is responsible for parsing a query, creating a query plan, and managing workers. Workers communicate with the data source to obtain the data they need to complete their assigned tasks. The connector carries out the specific operations required to provide the data to Trino as a table.
Separation of compute from storage. Starburst is a data lake analytics platform that allows you to federate data from multiple data sources and perform data lake analytics. One way Starburst platforms accomplish this is by separating compute from storage. This increases the availability and scalability of data and can reduce data storage and egress costs markedly because there is no longer need to process or duplicate data for storage in a data warehouse.
Catalogs
Catalogs control how Starburst connects to particular data sources. The distinction between a connector and a catalog is an important one. Whereas a connector allows you to connect to different types of data sources, a catalog includes the configuration information necessary to connect to a specific source.

Cross Cloud environments
Starburst allows to connect to storages and databases located in different cloud environments.
Performance Features
Managed statistics
You can configure Starburst Enterprise platform (SEP) to collect and store its own managed Table statistics for some data sources that only collect or expose a limited number of statistics. These additional statistics can then enable the query planner to make better-informed, cost-based optimizations.
Pushdown (system.query)
Trino can push down the processing of queries, or parts of queries, into the connected data source. This means that a specific predicate, aggregation function, or other operation, is passed through to the underlying database or storage system for processing.
The results of this pushdown can include the following benefits:
- Improved overall query performance
- Reduced network traffic between Trino and the data source
- Reduced load on the remote data source
These benefits often result in significant cost reduction.
Support for pushdown is specific to each connector and the relevant underlying database or storage system.
Cost-based Optimization
Trino supports several cost based optimizations:
- Join enumeration uses Table statistics provided by connectors to estimate the costs for different join orders and automatically picks the join order with the lowest computed costs.
- Join distribution selection. Trino automatically chooses whether to use a partitioned join (each node builds a hash table from only a fraction of the data) or broadcast join (hash table from all of the data; data is replicated to each node).
- Syntactic join order will be used if not using cost-based optimization. In this case it is optimal to syntactically order joins in your SQL queries from the largest tables to the smallest, as this minimizes memory usage.
Autoscaling with graceful scaledown
Using this feature the worker enters a special state in which it stops processing new requests, and shuts down after finishing to process current requests.
Materialized views
Materialized views in Hive allow you to access the results of a query from any data catalog you have defined in SEP in real time without re-processing the query, and with a refresh scheme that works best for your organization.
Materialized views must be enabled in the Hive catalog that they are accessed from. In addition, you must specify a schema to contain materialized view storage.
Note. Views in Iceberg catalog have many limitations, so better to create materialized views in Hive catalog.
Starburst Warp Speed
Starburst Warp Speed transparently adds an indexing and caching layer to enable higher performance for catalogs using the Hive, Iceberg, or Delta Lake connectors.
Warp Speed leverages patented indexing technology that autonomously identifies and caches the most used or most relevant data based on usage patterns, while the rest of the data remains close to the source, optimizing data lake performance.
Indexes are automatically created based on query patterns, minimizing the execution of full table scans. This is especially useful for workloads that have an extensive set of filtering predicates or selective filters in queries that return a relatively small number of rows.
Under the hood, Warp Speed manages index and cache elements on the cluster’s SSDs in a proprietary format.
Starburst Warp Speed uses different types of acceleration to improve query processing performance:
- Data cache acceleration
- Index acceleration
- Text search acceleration
Autonomous Indexing and Smart Caching
There is some additional functionality in Starburst does automatically indexing of information which is important to increase performance.
Starburst Cached Views/Table Scan Redirections
Starburst Cached Views is set of features which includes table scan redirection which allows read operations in a source catalog to be transparently replaced by reading the data from another catalog, the target catalog.
Components:
- Table scan redirection enables Starburst to offload data from tables accessed in one catalog to equivalent tables accessed in another catalog. This can improve performance by shifting data access to a more performant system. It can also reduce load on a data source.
- Starburst’s cache service provides the ability to configure and automate the management of table scan redirections. The service connects to an existing Starburst installation to run queries for copying data from the source catalog to the target catalog. The target catalog is regularly synchronized with the source and used as a cache.
Table scan redirections (system.query) allow you to transparently redirect queries to a cached version in a location that incurs lower egress costs, is more performant, or both.
Table scan redirections offer even finer-grained control for refreshes than do materialized views, including cleanup options.
Types of table scan refresh:
- Incremental refresh – more performant, but not suitable for all source tables and data modifications (modifications or deletions of existing rows are ignored).
- Full refresh – results in all the rows from the specified columns of the source table getting loaded into the cached table.
Disadvantages of table scan redirect:
- Does not support incremental refresh with updates and deletes.
- If you make changes to list of tables/columns which use Table Scan Redirection, you will need to restart Starburst cluster.
Dynamic Filtering
Dynamic filtering optimizations significantly improve the performance of queries with selective joins by avoiding reading of data that would be filtered by join condition. In this respect, dynamic filtering is similar to join pushdown discussed above, however it is the equivalent of inner join pushdown across data sources. As a consequence we derive the performance benefits associated with selective joins when performing federated queries. That significantly boosts the performance of query federation use cases.
Usage Features
Data Products
Data product in Starburst Galaxy is a package of business and technical metadata that includes a pointer to the underlying dataset. Data product is a container with one or more datasets in the Gravity layer. Users interact with all these components as a single entity, creating an efficient, scalable wrapper. This wrapper can be saved, published, and shared.
This empowers data teams to provide value-add information enabling greater self-serve analytics capabilities for the organization, greatly reducing the overhead on data teams, and enabling consumers to more quickly and efficiently generate reports, dashboards, and insights.
When used in conjunction with other Gravity-level features, data products enable:
- Easy discoverability with universal search
- Fine-grained security when the coupled with built-in access control policies
- Immutable history via audit trails and query history
- Domain ownership by allowing teams to utilize and leverage their own data infrastructure (more on this later)
Incremental Updates
To incrementally load large tables with Updates/Deletes in the source, you can use MERGE statement, which is available on top of Iceberg catalogs. The process will be following:
- Complete initial load of large table to the destination table in Iceberg catalog.
- When you need to update records, load changes from the source (for example, records changed since yesterday) to separate delta table.
- Use MERGE statement to apply change from delta table to destination table.
Time Travel
Uses benefit of Iceberg storage.
Security
Security between the cluster and data sources is highly dependent upon organization’s networking and the location of the data sources relative to the cluster.
Both Starburst Galaxy and Starburst Enterprise provide built-in role-based access control for data sources. Starburst Enterprise can, alternatively, integrate with Privacera, Immuta or Apache Ranger for third-party role-based access control (RBAC) for data sources.
The built-in access control works alongside supported third-party RBAC systems to provide access control for the web UI:

Reference Materials
- Starburst Data Lakehouse Resource Center
- Starburst Enterprise Docs:
- Starburst connectors feature matrix (Starburst Enterprise vs Trino)
